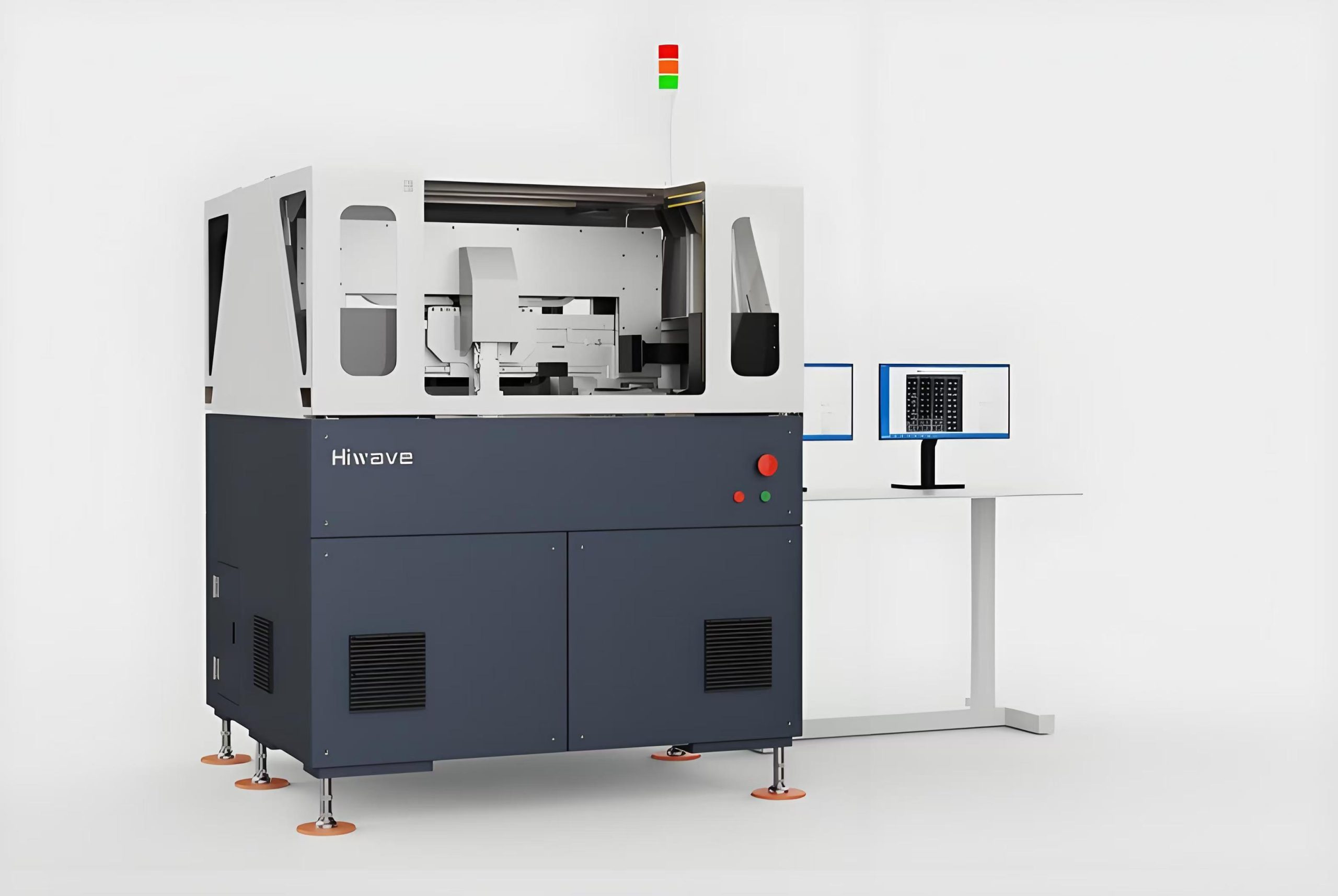
Comprehensive Analysis of Misjudgment Factors in Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAT & SAM)
views:694
author:admin
source:Hiwave
time:2025-03-25
catogory:Frequently Asked Questions
Ultrasonic scanning (including SAT and C-SAM technologies), as a non-destructive testing method, has been widely used in the quality inspection of integrated circuit……
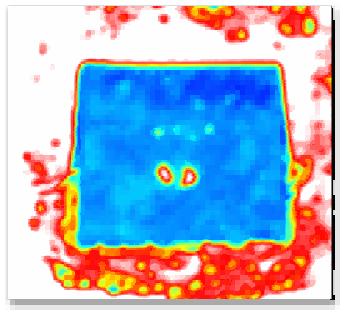
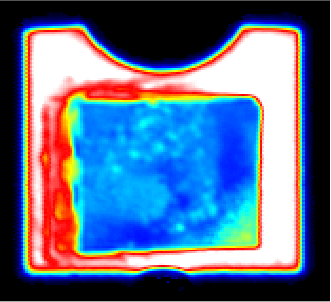
Ultrasonic scanning (including SAT and C-SAM technologies), as a non-destructive testing method, has been widely used in the quality inspection of integrated circuit and discrete device packaging due to its advantages of high sensitivity, high resolution, and real-time imaging. However, ensuring the reliability of the test results must be based on strict procedural standards. From a professional perspective, it is necessary to identify and avoid numerous factors that may lead to misjudgment. A lack of understanding of these factors can significantly increase the risks of imaging distortion and defect omission. Misjudgments in ultrasonic scanning are mainly influenced by material types, defect categories, equipment conditions, and operational subjectivity. The following sections will elaborate on these factors in detail.