Ultrasonic Testing
views:1,055
author:admin
source:Hiwave
time:2025-01-02
catogory:Frequently Asked Questions
Basic Principle of Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing is a method that uses ultrasonic wave technology to perf……
Ultrasonic testing is a method that uses ultrasonic wave technology to perform inspections. Ultrasound refers to sound waves with a frequency greater than 20,000 Hz. These waves have good directionality, can propagate in a straight line through a medium, and exhibit characteristics such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, and attenuation when they encounter different media or structural interfaces. These characteristics make ultrasonic testing useful for detecting internal defects in materials, such as cracks, inclusions, and voids.
Applications of Ultrasonic Testing
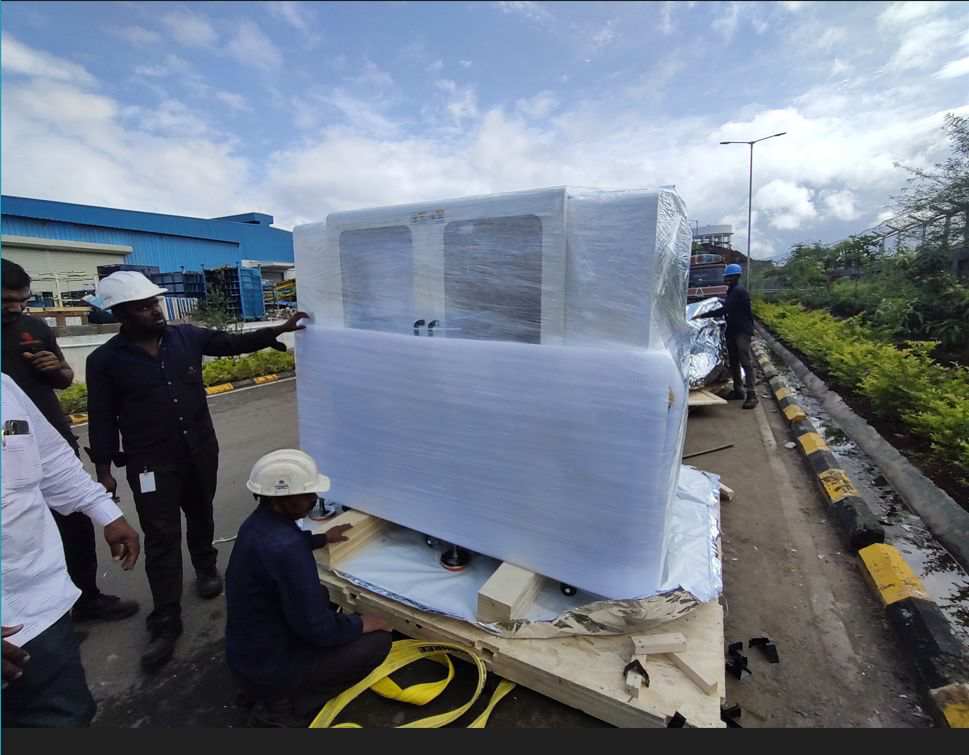
Ultrasonic testing is widely used in industrial fields, particularly for the inspection of materials, components, and equipment. It can be applied in various aspects such as quality control during product manufacturing, raw material inspection, process improvement, and is also an indispensable tool in equipment maintenance. Ultrasonic testing is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, non-metals, and composite materials. Examples include steel plates, forged steel, aluminum and aluminum alloy plates, titanium and titanium alloy plates, composite panels, and the inspection of butt welded joints.
Main Advantages of Ultrasonic Testing
Hiwave is a high-tech company in China focused on the research and development, system integration, sales, and technical services of Scanning Acoustic Microscopes (SAM). With outstanding technical capabilities and extensive industry experience, the company provides advanced non-destructive testing solutions to global clients, with applications in high-demand fields such as semiconductors, IGBT modules, diamond materials, water-cooled heat dissipation systems, electronics and electrical appliances, and composite materials.
Technology and Product Advantages
Core Technology: Hiwave has mastered the core technologies of ultrasonic imaging, including high-resolution ultrasonic transducer design, multi-channel data acquisition systems, and real-time image processing algorithms. These technologies ensure that the company’s products lead the industry in detection accuracy, speed, and reliability.